Exploring the Medicinal Benefits of Elderberry

Looking for a natural remedy that has a long history of medicinal use? There’s evidence that the elderberry plant may have been cultivated by prehistoric man. There are also recipes for elderberry-based medications dating back to Ancient Egypt.
However, most historians typically trace its healing abilities back to Hippocrates, the ancient Greek known as the “Father of Medicine,” who described the plant as his “medicine chest” because of the wide array of health concerns it seemed to treat. Whether we’re talking cavemen, ancient Egyptians or ancient Greeks, this remedy definitely goes way back, which is why it’s no wonder it’s known as one of the top antiviral herbs on the planet.
Health benefits of the elder plant include naturally improving:
- sinus issues
- nerve pain
- inflammation
- chronic fatigue
- allergies
- constipation
- even cancer
Research published in the Journal of International Medical Research suggests that when it’s used within the first 48 hours of onset of symptoms, the plant may even help relieve and shorten the duration of cold and flu. For this reason, the government actually employed the use of elderberry to fight the flu during the 1995 Panama flu epidemic.
Does it really work? What exactly does it do, and how can you use it to promote better health?
Here’s what you need to know, including its many benefits.
What Is Elderberry?
Sambucus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Adoxaceae. The different species of Sambucus are commonly called elderberry or elder. The berries and flowers of the elder plant are used as medicine.
Elderberry is native to Europe, Africa and parts of Asia, but it’s become common in the U.S. It has deciduous leaves, white flowers (elderflowers) and berries that turn from green to red to black when ripe.
Elder is commonly found growing in woodlands and hedgerows.
Sambucus nigra is the full scientific name of the most common variety used for medicinal purposes, as well as the species on which the majority of scientific research has been conducted. It’s a deciduous tree growing up to 32 feet tall with cream-white flowers and blue-black berries.
Other common names for Sambucus nigra include black elder, European elder, European elderberry and European black elderberry. The elderberry bush or elderberry tree yields the berries that are commonly used in syrups, jams and wine, among other medicinal and culinary delights.
In addition to black elderberry, there are several other varieties available as well. Some of the most common include:
- Black lace elderberry
- Red elderberry
- Adams elderberry
- Lemon lace elderberry
- Black beauty elderberry
- Blue elderberry
- York elderberry
European elder flowers contain approximately 0.3 percent of an essential oil composed of free fatty acids and alkanes. The triterpenes alpha- and beta-amyrin, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, betulin, betulinic acid and a variety of other minor components have been identified.
Elderberry fruit contains quercetin, kaempferol, rutin and phenolic acids. It also contains flavonoids, which have antioxidant properties that can help prevent cell damage, and anthocyanidins, which are chemical compounds that are known to have immune-boosting properties.
The raw berries are made up of 80 percent water, 18 percent carbohydrates, and less than 1 percent each of protein and fat. Elderberries are naturally high in vitamin C, vitamin A, vitamin B6, iron and potassium, among several other essential nutrients.
Benefits
1. Provides Cold and Flu Relief
One of the most well-studied elderberry supplement benefits is its powerful immune-boosting properties. The berries contain chemical compounds called anthocyanidins, which have been found to possess immunostimulant properties.
Research actually shows that elderberry is a safe, efficient and cost-effective treatment for the common cold and flu. A 2021 systematic review screened 1,187 records and five randomized trials on elderberry for the treatment or prevention of viral respiratory illness. Researchers found that elderberry may reduce the duration and severity of symptoms related to colds and influenza, and there’s no evidence that it overstimulates the immune system.
A 2016 study published in Nutrients showed that elderberry supplementation was able to reduce cold duration and symptoms in people using air travel. People using this herb from 10 days before travel until four to five days after arrival overseas experienced, on average, a two-day shorter duration of their colds as well as a noticeable reduction in cold symptoms.
Several studies have found benefits to support the use of elderberry for flu symptoms as well. Specifically, the flavonoids in the berries bind to the H1N1 human influenza virus as well as the H5N1 avian influenza virus.
A 2009 study randomized patients into two groups. One group was given four doses of 175-milligram proprietary elderberry extract daily, and the other group received a placebo for two days.
The group treated showed significant improvement in most signs of flu, while the placebo group showed no improvement in symptom severity. Researchers concluded that the extract is effective in controlling influenza symptoms.
Another study published in the Journal of International Medical Research referenced above suggests that when elderberry is used within the first 48 hours of the onset of signs of flu, it can shorten the duration of flu symptoms by an average of four days.
2. Reduces Sinus Infection Symptoms
With elderberry’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, it makes sense that it can help treat sinus issues and diseases related to respiratory health. A sinus infection is a condition in which the cavities around the nasal passages become inflamed, and this antiviral herb has promise as a sinus infection remedy.
A study conducted by the Institute of Complementary Medicine’s Department of Internal Medicine at the University Hospital in Zurich, Switzerland examined the use of a product called Sinupret, which contains elderberry extract. The researchers used Sinupret to treat bacterial sinusitis along with an antibiotic (doxycycline or vibramycin) and a decongestant. Interestingly enough, those who took the combination did better compared to those who did not take Sinupret at all.
3. Lowers Blood Sugar
Both the elder flower and the berry have traditionally been used to treat diabetes. Research has confirmed that extracts of elderflower stimulate glucose metabolism and the secretion of insulin, which could potentially help lower blood sugar levels.
Research published in the Journal of Nutrition evaluated black elderberry’s insulin-like and insulin-releasing actions in vitro. The study found that an aqueous extract of elder significantly increased glucose transport, glucose oxidation and glycogenesis without any added insulin.
Glycogenesis is the process by which excess sugar is cleared out of the bloodstream and into your muscles and liver to help maintain normal blood sugar.
Furthermore, a 2017 animal study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences noted that elderberries can serve as a potential source of bioactive compounds for formulations used for the management of diabetes. Researchers found that both lipophilic and polar extracts of the berry lowered insulin resistance in rats with type 2 diabetes.
4. Acts as a Natural Diuretic
A diuretic is a substance that promotes the production of urine. Research indicates that elder leaves, flowers and berries were used for their diuretic properties in rural populations as natural medicine. Even the bark of the plant was used for its diuretic and slimming effects.
Doctors prescribe diuretics when the body retains too much fluid, which is a common problem in older adults. Thanks to its ability to act as a safe diuretic, elderberry has been shown to promote both urination and bowel moments to help protect against fluid retention.

5. Promotes Regularity
In traditional or folk medicine, the elder plant was used as a laxative to relieve constipation. It was added to herbal mixtures to improve regularity.
Some research suggests that elderberry tea benefits constipation and can help support regularity and digestive health. A small, randomized trial found that a specific compound containing elderberries along with several other plants could act as an effective natural laxative for the treatment of constipation.
Unfortunately, however, there are currently no studies evaluating elderberry itself for constipation relief, so more research is still needed.
6. Supports Skin Health
Elderberry has made its way into cosmetic products, and for good reason. Its content of bioflavonoids, antioxidants and vitamin A makes it awesome for skin health. Not only that, but researchers also suspect that a compound found in the berry could give a natural boost to skin.
Anthocyanin is a type of natural plant pigment found in elderberry that has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Some researchers suspect that this compound may improve skin’s structure and condition to enhance overall skin health.
7. Eases Allergies
In addition to using elderberry syrup for colds, the flowers of the elder plant are also known to be an effective herbal allergy remedy. Since allergies involve an overreaction of the immune system as well as inflammation, research suggests that the herb’s ability to improve immune function and calm inflammation can help provide allergy relief.
Some herbalists put black elder flower on the list of most effective herbs used for treating hay fever-like symptoms. It can be used for allergies on its own or in combination with other herbs and natural remedies.
8. Could Have Cancer-Fighting Effects
Edible berry extracts like elderberry extract are rich in anthocyanins and have been shown to have a broad spectrum of therapeutic, pharmacologic and anti-carcinogenic properties. In vitro studies specifically indicate that the elderberry has some chemopreventive properties, which can help inhibit, delay or reverse cancer formation.
One study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food compared the anticancer properties of European and American elderberry fruits. European elderberry (Sambucus nigra) is known for its medicinal use and contains anthocyanins, flavonoids and other polyphenolics, which all contribute to the high-antioxidant capacity of its berries. American elderberry (Sambucus canadensis) has not been grown or promoted as a medicinal plant like its European relative.
This study tested extracts of both berries to assess anticancer potential and found that both demonstrated significant chemopreventive potential. Additionally, the American elder extract showed inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase, which is an enzyme marker related to the promotion stage of cancer formation.
Thus, elderberries show potential as cancer-fighting foods.
9. May Improve Heart Health
Although studies have found mixed results, some research suggests that elderberry extract may improve heart health.
For example, one animal model showed that giving mice with high cholesterol and HDL cholesterol dysfunction anthocyanin-rich black elderberry extract helped reduce hepatic cholesterol levels and improved HDL function. This may be due to the presence of anthocyanins, which are polyphenols that have demonstrated antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
Another study found that elderberry extract may have beneficial effects on high blood pressure. When polyphenols extracted from the plant were administered with renin inhibitors to rats with hypertension, they reduced arterial pressure.
Researchers suggest that using polyphenols to lower blood pressure may also help reduce the side effects of blood pressure-lowering medications and improve overall quality of life.
Related: 10 Holy Basil Benefits: Tulsi Helps Anxiety, Acne & More
How to Use
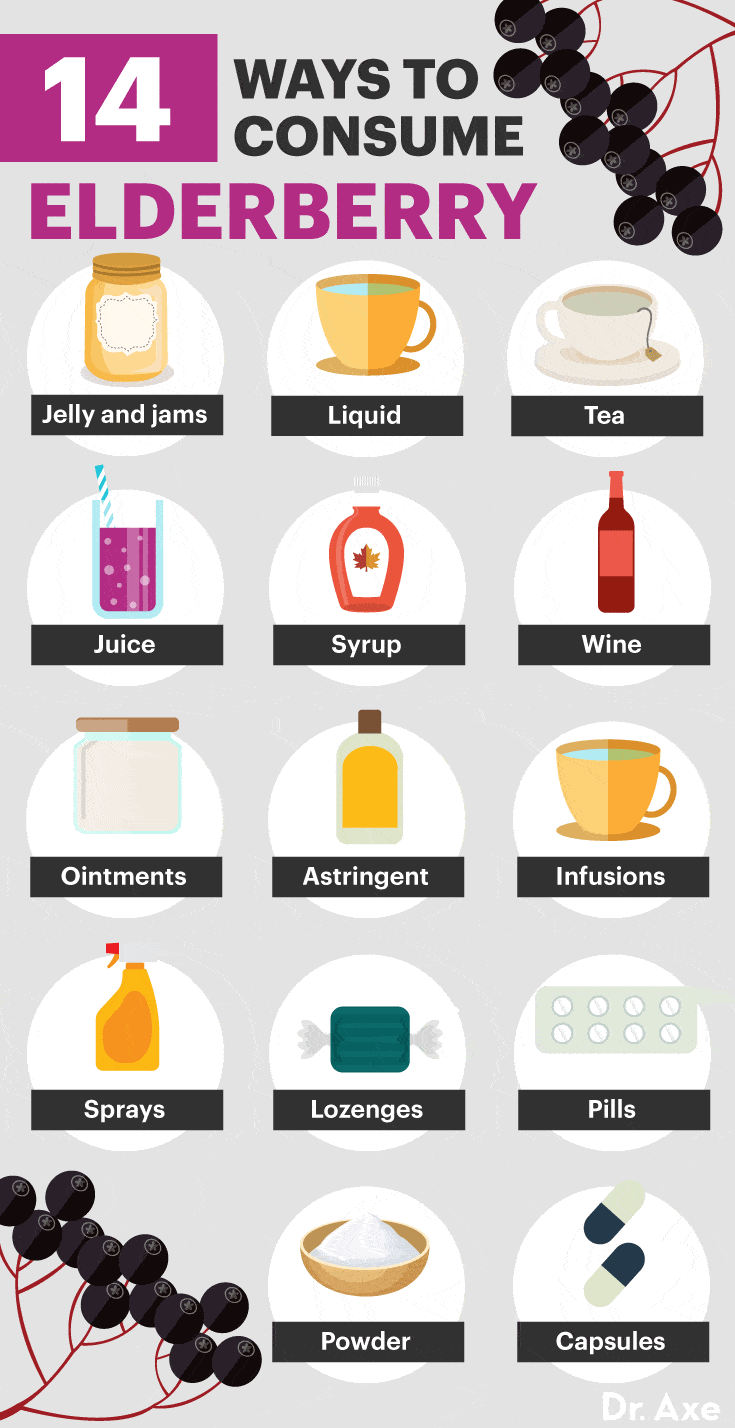
Wondering where to buy elderberry and how to start adding it to your diet? It is available at many local health stores and online retailers and can be purchased in a variety of different forms.
Elderberry gummies, elderberry wine and elderberry juice are all popular options for getting your fix of this incredible ingredient.
When it comes to colds, flu and upper respiratory issues, elderberry syrup is very popular. There are high-quality brands readily available for purchase, or you can find many online resources for how to make elderberry syrup to try making it at home.
Most elderberry syrup recipe options out there involve simmering elderberries with a bit of water and a variety of other healing herbs for 45 minutes to an hour.
Elderberry tea is another great option, especially if you use elderberry for flu and cold symptoms. You can either buy tea bags or purchase dried berries or flowers and make a tea by combining one tablespoon of berries or flowers with eight ounces of water. Try adding lemon, cinnamon or mint to give the flavor and health benefits a hearty boost.
Not a fan of hot teas or black elderberry syrup? Then you can try elderberry juice, which is sweet, tart and refreshing. Just be sure not to purchase one that has too much added sugar.
Risks, Side Effects and Interactions
Despite the many health benefits associated with this medicinal plant, there are several elderberry side effects to consider as well.
Ripe, cooked berries from most of the Sambucus species are edible. However, you should not consume raw berries or other parts of the plant since they contain a cyanide-inducing chemical, which can result in nausea, vomiting or diarrhea.
Generally, commercial preparations don’t cause adverse reactions when used at recommended dosages.
Elderberry appears to have few side effects when used properly for short periods of time of up to five days. Occasionally, however, elderflowers and elderberries can cause allergic reactions.
Discontinue use if you have a mild allergic reaction, and seek medical attention if you have a serious allergic reaction.
Using elderberry supplements for kids is not recommended unless you’ve consulted with your pediatrician. If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, don’t take this herb, as research is lacking on its effects on fetal health and development.
If you have an autoimmune disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, ask your doctor before taking elderberry supplements because it may stimulate the immune system. If you have any other ongoing health concerns, talk with your health care provider before taking it as well. People with organ transplants should not take elderberry.
Because of its powerful effects on health, elderberry supplements could potentially interact with several medications. If you currently take any of the following medications, you should talk to your health care provider before using an elderberry supplement or any other elder plant products:
- Diabetes medications
- Diuretics (water pills)
- Chemotherapy
- Immunosuppressants, including corticosteroids (prednisone), and medications used to treat autoimmune diseases
- Laxatives
- Theophylline (TheoDur)
Conclusion
- Elderberry is a type of plant that is cultivated for its medicinal properties and used to treat a variety of conditions.
- What are the benefits of elderberry? It may provide relief from the common cold and flu, as well as allergies and sinus infections. It may also help lower blood sugar, improve heart health, support healthy skin and act as a natural diuretic.
- This herb is available in syrup, juice and tea form. Supplements can be purchased at many health stores or made at home.
- What are the side effects of elderberry? Although commercial preparations are generally safe for consumption, eating raw elderberry may cause symptoms like nausea, diarrhea and vomiting.
- Using this antiviral herb is not recommended for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, children, or those with autoimmune disorders.
- Does elderberry interact with medications? If you’re on chemotherapy or take diabetes medications, diuretics, immunosuppressants, laxatives or other medications, talk to your doctor before starting supplementation.





Leave a comment