The Medicinal Uses of Olive Leaf
Olive Leaf Extract Benefits for Cardiovascular Health and Brain Function
Olive Leaf
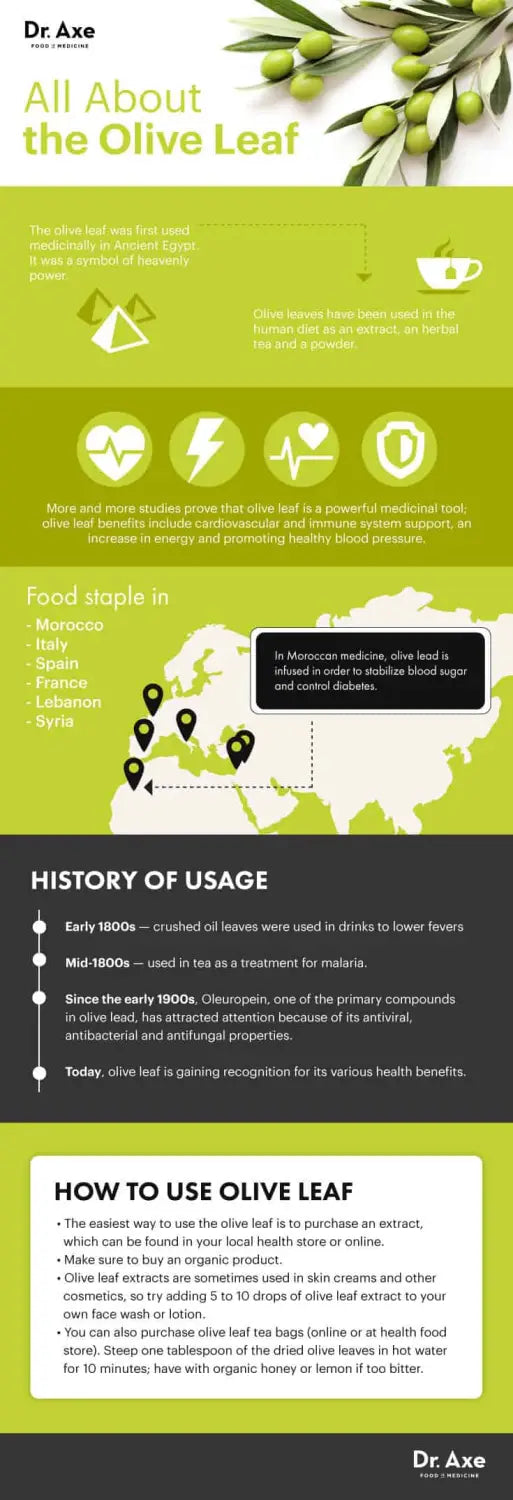
The olive leaf was first used medicinally in Ancient Egypt, where it served as a symbol of heavenly power. Since then, olive leaves have been used therapeutically in the human diet as an extract, herbal tea and powder.
Olive leaf contains many potentially bioactive compounds that have antioxidant, antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory and hypoglycemic properties — similar to the well-known olive oil benefits.
More and more studies are proving that olive leaf extract is a powerful medicinal tool, with benefits including immune system support, increased energy and promoting healthy blood pressure. Because of the promising scientific studies indicating its medicinal potential, olive leaf continues to gain recognition for its various health benefits.

What Is Olive Leaf Extract?
Olive leaf extract comes from the leaves of the olive tree, called Olea europaea. The olive tree is part of the Oleaceae family, which also includes species such as lilacs, jasmine, Forsythia and the true ash trees. It’s an evergreen tea or shrub that’s native to Asia, Africa and the Mediterranean. Researchers believe that the olive tree had its origin approximately 6,000–7,000 years ago in the region corresponding to ancient Persia and Mesopotamia.
Typically a short tree that rarely exceeds 26 to 49 feet in height, the olive tree flowers are small, white and feathery, and the leaves are a silver-green color. The olives are harvested in the green-to-purple stage and the seed of the olive is commonly referred to as the pit, and in Britain, it’s called a stone.
In the early 1800s, crushed olive leaves were used in drinks to lower fevers, and a few decades later, they were used in tea as a treatment for malaria. In Moroccan medicine, olive leaf is infused in order to stabilize blood sugar and control diabetes. These medicinal benefits of olive leaf extract comes from the plants powerful compounds.
One bioactive compound present in olive leaves is the secoiridoid oleuropein, which can constitute up to 6–9 percent of dry matter in the leaves. Other bioactive components include secoiridoids, flavonoids and triterpenes. These are plant metabolites that provide health benefits through cell signaling pathways and antioxidant effects.
Oleuropein, one of the primary compounds in olive leaf, has attracted attention since the early 1900s because of its antiviral, antibacterial and antifungal properties. Studies have found that oleuropein, which is a polyphenol, is a potent antioxidant that helps to lower blood pressure naturally and prevent cardiovascular disease. Oleuropein also displayed anti-cancer functions when it made tumors in animals regress or disappear.
Health Benefits
1. Lowers Blood Pressure
A 2011 study evaluated the effectiveness of olive leaf extract in comparison to Captopril, a medication that is given to patients with hypertension or high blood pressure. Five hundred milligrams of olive leaf extract, taken twice daily for eight weeks, significantly reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
While both olive leaf extracts and Captopril were able to prevent high blood pressure levels, the olive leaf treatment also resulted in a reduction of triglyceride levels (reducing bad cholesterol); plus, unlike olive leaf, there are a number of possible side effects when taking Captopril, including dizziness, loss of taste and dry cough.
2. Improves Cardiovascular Health
Olive leaves have been used as an herbal tonic to support cardiovascular function for thousands of years. High doses of olive leaf extract have been shown to help reduce elevated LDL-cholesterol levels and assist in the maintenance of normal blood pressure.
Oleuropein, the main glycoside present in olive leaf, and hydroxytyrosol, the principal product of oleuropein that is present in olives and olive leaf extract, have both been linked to reduction of coronary heart disease and certain cancers.
A study done at the School of Biomedical Sciences in Australia examined rats that were fed a high fat and high carbohydrate diet for 16 weeks. The rats that were not treated developed signs of elevated abdominal and hepatic fat deposition, collagen deposition in heart and liver, cardiac stiffness and oxidative stress markers.
The rats that were treated with olive leaf extracts had improved or normalized cardiovascular, hepatic (liver function) and metabolic signs. This study suggests that olive leaf extracts may be able to reverse cardiovascular stress and chronic, disease-causing inflammation in humans.
3. Fights Diabetes
One study conducted in Greece measured the effects of olive leaf extracts on the formation of advanced glycation end products (known as AGEs), which are substances that can be a factor in the development of diabetes and many other chronic diseases. Inhibiting AGE formation is a preventive and therapeutic target for patients with diabetes, and a 2013 study found that olive leaf extract did just that, working to improve diabetes symptoms naturally.
Olive leaf extracts have hypoglycemic effects, meaning they reduce blood sugar levels in the body. The olive leaf also controls blood glucose levels in the body. The polyphenols in olive leaf play a vital role in delaying the production of sugar, which causes inflammatory diseases like diabetes.
A 2017 review published in Molecules found evidence to confirm the interactions and combined benefits of olive polyphenols that are found in olive leaf extracts. These polyphenols were able to induce an improvement in blood glucose in prediabetes.
There’s also some evidence on animals to suggest that olive leaf may aid weight loss by regulating the expression of certain genes that role a role in weight gain. But to be sure about olive leaf for weight loss, more research is needed.
4. May Reduce the Risk of Cancer
Olive leaves may play an important role in fighting cancer because of their ability to stop the angiogenic process, which stimulates the growth of tumors. The compound oleuropein has an antioxidant and anti-angiogenic effect by inhibiting the reproduction and migration of advanced tumor cells.
A 2009 study conducted in Greece showed, for the first time, that olive leaf extracts have strong antioxidant potency and inhibit cancer and endothelial cell reproduction. Olive leaf extracts slowed the growth of cells associated with breast cancer, urinary bladder cancer and brain cancer.
5. Improves Brain Function
Another olive leaf benefit is its positive effects on brain function. Studies show that oleuropein, one of the main components in olive leaf, reduces the symptoms or occurrence of age-related disorders, such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Research suggests that there is a connection between free radicals and Alzheimer’s. Because olive leaf is an antioxidant, it helps to combat the damage caused by free radicals and protects the brain from memory loss. Using olive leaf infusions or extracts is a safe and effective way to treat Alzheimer’s disease naturally.
An in vivo study published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity found that oleuropein is able to induce autophagy, achieving a decrease of aggregated proteins and a reduction of cognitive impairment. Basically, this means that because of this compound, olive leaf extract promotes the orderly degradation and recycling of our cellular components.
6. Treats Arthritis
Arthritis is a joint disease that causes swelling and pain in the joints. The key word here is swelling — which means inflammation. Because the olive leaf is an anti-inflammatory agent, it works as a natural arthritis remedy.
A 2012 study found that olive leaf extracts significantly reduced paw swelling in rats with arthritis; this is because the extracts were able to reduce the inflammation that was present in the joints. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, impacting more than 33 million American adults. This occurs when the cartilage between the bones and the joint wears down, which allows the bones to rub together rather than giving them the protection and cushion of cartilage.
Studies have shown that olive leaf extracts cuts down on the chronic pain that is associated with osteoarthritis, and it reduces the production of cytokines and enzymes that are markers for the inflammatory process.
7. Kills Bacteria and Fungi
An important olive leaf benefit is its ability to fight off infections, including candida infections, meningitis, pneumonia, chronic fatigue, hepatitis B, malaria, gonorrhea, shingles and tuberculosis. It also naturally treats ear, dental and urinary tract infections.
A study done in 2003 proved that olive leave extracts have an antimicrobial effect against bacteria and fungi. This suggests that olive leaf works as a natural antibiotic, due to it’s ability to fight some bacterial infections. In the study, the olive leaf extracts killed almost all bacteria tested, including dermatophytes (causing infections on the skin, hair and nails), candida albicans (an agent of oral and genital infections) and Escherichia coli cells (bacteria found in the lower intestine).
And a 2017 study found that olive leaf extract works as an antimicrobial agent that controls foodborne pathogens, including E. coli and salmonella.
8. Boosts Immune System
The olive leaf has antiviral properties, giving it the ability to fight or prevent the common cold, as well as treat dangerous viruses. Research shows that olive leaf extracts effectively fight against a number of disease-causing microbes, including some of the viruses that cause influenza and other respiratory infections.
The powerful compounds found in olive leaves destroy invading organisms and don’t allow viruses to replicate and cause an infection. In fact, the olive leaf is so beneficial to our health that treatment with olive leaf extracts reversed many HIV-1 infection-associated changes in a study done at the New York University School of Medicine.
And a 2019 study found that when olive leaf extract was given to high school athletes for nine weeks during their competitive season, there was a significant 28 percent reduction in sick days taken by those supplementing with olive leaf.
9. Protects Skin
Olive leaf has the power to reverse years of damage to your skin and the signs of aging. Because of olive leaf’s antioxidant properties, it helps to prevent certain types of cell damage, especially those caused by oxidation. Foods and herbs that contain antioxidants are great tools for the health of your skin and cells.
The Division of Biochemical Pharmacology in Japan found that olive leaf extract, when given to mice with UV radiation damage, decreased skin thickness and skin elasticity, which are signs of skin damage. The treatment also inhibited skin carcinogenesis and tumor growth.
Some more olive leaf benefits may include:
- more energy
- toothache relief
- diminished food cravings
- joint pain relief
- heartbeat regulation
- improved wound healing
Uses
The easiest way to receive olive leaf benefits is to purchase an extract, which can be found in your local health store or online. Make sure to buy an organic product to assure that it doesn’t include pesticides.
Olive leaf extracts are sometimes used in skin creams and other cosmetics, so you can also try adding 5 to 10 drops of olive leaf extract to your own face wash or lotion to take advantage of the olive leaf benefits for skin.
How long does it take for olive leaf extract to work? The results will vary depending on your health goals, but studies using olive leaf show that it’s effective within 8 weeks.
Here are some simple ways to use olive leaf extract at home:
- Olive leaf extract for skin care: Because of its anti-aging and bacteria-fighting capabilities, you can use olive leaf extract to make a skin-clearing face wash like my Homemade Honey Face Wash. Try adding 5–10 drops of olive leaf extract to my Homemade Body Butter Lotion — it’s completely natural and free of any harmful chemicals. If you are using olive leaf extract for herpes or another skin issue, simply add a high-quality extract to a cotton ball and rub it into the area of concern.
- Olive leaf extract for oral health: Olive leaf has strong antibacterial properties, making it great for fighting infections in your mouth too. Try adding five drops of olive leaf extract to this Homemade Remineralizing Toothpaste.
- Olive leaf capsules: Olive leaf extract is also available in capsule and soft gel forms. Capsules can be taken to support immune function and provide powerful antioxidants. Capsules can also be taken to promote cardiovascular health. The standard olive leaf extract dose ranges from 500-1,000 milligrams daily. It’s best to divide your daily dosage into 2-3 smaller doses and take it with a meal or snack.
- Olive leaf tea for immunity: Olive leaf tea is available in your local health food store and online. You can drink olive leaf tea daily to boost immune function and reduce inflammation. If you have access to an olive tree, then you can use the leaves to make tea. Start by washing the leaves thoroughly, then bake them at about 150 degrees or below until they are dry. Then crush the dry leaves and remove the stalks. Steep one tablespoon of the dried olive leaves in hot water for 10 minutes; drink a cup (or more) a day to get all of these amazing olive leaf benefits. If the taste it too bitter for you, add some organic honey or lemon.
Risks, Side Effects and Interactions
What are the side effects of olive leaf extract? When olive leaf is used in appropriate amounts, it is generally safe. However, on occasion, olive leaf extract may cause dizziness in people who have low blood pressure because it can lower it even further.
Olive leaf may also cause stomach irritations, especially if the dose is too high or the olive leaf tea is too strong. If that happens, dilute the extract with a carrier oil like coconut oil, or add extra water to the tea. Some other side effects may include diarrhea, acid reflux, headache, stomach pain and heartburn.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, do not take olive leaf extract unless it is under the guidance of your physician. There is not enough research to prove that it is safe under these circumstances.
Do not take olive leaf with blood pressure medications since it lowers blood pressure. Olive leaf extract demonstrates hypoglycaemic and antidiabetic properties, so if you are on diabetic medication, start with small doses under the guidance of your healthcare professional to ensure that you will not have a reaction. It’s a good idea to speak to your physician beforehand, especially if you have diabetes and are trying olive leaf for the first time.
Olive leaf extract may increase the effect of blood thinners, such as Warfarin. This is because olive leaf may prevent blood platelets from sticking together. If you are taking Warfarin or other blood thinners, check with your physician before taking olive leaf extract.
And if you are undergoing chemotherapy treatment, speak to your healthcare professional before using olive leaf, as it may interfere with some chemotherapy drugs.
Final Thoughts
- Olive leaf has been used medicinally since ancient times, when the Egyptians viewed it as a symptom of heavenly power. Today, olive leaf extract, tinctures, capsules and teas are therapeutically and medicinally by people around the world.
- What is olive leaf extract good for? It’s commonly used to reduce inflammation, boost immune function, fight infections and promote cardiovascular health. It can also be used topically to fight skin issues and orally to boost oral health.
- When it comes to olive leaf dosage, it ranges from 500–1,000 milligrams daily. It is generally safe to take olive leaf extract everyday under the guidance of your healthcare professional. Some people may experience olive leaf side effects like stomach pain, headaches, dizziness, heartburn and diarrhea.
What is Olive Leaf?
Olive Leaf, scientifically known as Olea europaea, is the leaf of the olive tree, which is native to the Mediterranean region and is also cultivated in various parts of the world. This leaf has been utilized for its medicinal properties for centuries.
What is the scientific name of Olive Leaf?
The scientific name of Olive Leaf is Olea europaea. This name is derived from its botanical classification, with “Olea” referring to the genus and “europaea” indicating its European origin.
Does Olive Leaf have other common names?
Olive Leaf is also known by several common names, including “Olive Tree Leaf,” “Olive Leaves,” and “Olea europaea leaf.” These names are often used interchangeably to refer to the leaves of the olive tree.
What is Olive Leaf’s traditional and modern medicinal use?
Olive Leaf has a rich history of traditional medicinal use. In the past, it was employed for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. It was also used to treat various ailments, including infections, high blood pressure, and digestive issues. In modern times, Olive Leaf has gained popularity for its potential health benefits, particularly as an antioxidant and for its role in supporting cardiovascular health. Some people use it as a dietary supplement to boost their immune system and manage blood pressure.
What nutrients (vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, etc.) does Olive Leaf contain?
Olive Leaves contain a variety of essential nutrients and bioactive compounds. They are a good source of vitamins such as vitamin C, vitamin A, and various B vitamins. Additionally, Olive Leaves are rich in minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. What makes Olive Leaf particularly interesting is its high content of antioxidants, including oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, and flavonoids. These antioxidants are known for their potential to combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, contributing to the leaf’s medicinal and health-promoting properties.
How should Olive Leaf be prepared or consumed (e.g., tea, tincture, capsules, tablets)?
Olive Leaf can be prepared and consumed in various forms, including tea, tinctures, capsules, and tablets. The choice of preparation depends on personal preference and the intended use. Olive leaf tea can be made by steeping dried leaves in hot water, while tinctures are concentrated liquid extracts. Capsules and tablets offer a convenient option for those who prefer a measured and consistent dose. Regardless of the form, it’s essential to follow the product-specific instructions for the best results.
Where is Olive Leaf usually sourced or cultivated?
Olive Leaf is primarily sourced and cultivated in Mediterranean countries, with Spain, Italy, Greece, and Tunisia being major producers. The trees from which the leaves are harvested, Olea europaea, thrive in the warm, sunny climates of these regions. The leaves are carefully harvested and processed to extract the beneficial compounds, and these products are often exported worldwide for various uses.
How does Olive Leaf taste, and can it be mixed with other herbs or foods for palatability?
Olive Leaf has a slightly bitter and earthy taste, which some people find challenging to consume on its own. To enhance its palatability, you can mix it with other herbs or foods. For example, you can blend it into a smoothie with fruits and vegetables, or infuse it into herbal tea with flavors like mint or lemon. Experimenting with different combinations can help make Olive Leaf more enjoyable to consume while retaining its potential health benefits.
What other supplements work well together with Olive Leaf?
Olive Leaf is a powerful herbal supplement with various health benefits, and it can be combined with other supplements to enhance its effects or address specific health goals. Here are some supplements that work well with Olive Leaf:
Garlic: Combining Olive Leaf with Garlic can help support heart health. Both supplements have been linked to maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Turmeric (Curcumin): Olive Leaf and Turmeric (specifically its active compound, curcumin) can have a synergistic effect on reducing inflammation and supporting the immune system. This combination is particularly beneficial for those seeking anti-inflammatory support.
Astragalus: Olive Leaf and Astragalus are both known for their immune-boosting properties. Combining them can provide comprehensive immune system support, helping the body defend against illnesses.
Probiotics: When combined with Olive Leaf, probiotics can aid in maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria. This combination can be especially useful for digestive health and overall well-being.
Vitamin C: Olive Leaf and Vitamin C can work together to strengthen the immune system. This combination is effective in promoting overall health, especially during cold and flu seasons.
Grape Seed Extract: Combining Olive Leaf with Grape Seed Extract can have antioxidant and cardiovascular benefits. Both supplements have been associated with improving blood flow and supporting heart health.
Milk Thistle: Olive Leaf and Milk Thistle can complement each other in promoting liver health. The combination may aid in detoxification and overall liver function.
L-lysine: Olive Leaf and L-lysine can be combined for their antiviral properties. This combination may be beneficial for those looking to support the body’s defense against viral infections.





Leave a comment