The Fascinating Process of Making Tea
How Tea is made
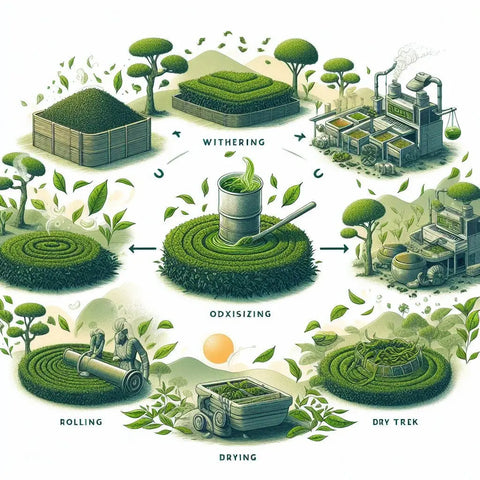
Tea is the most popular and demanded drink in the world. Its flavors and aroma have inspired people for centuries. Moreover, tea in itself is full of medical benefits. Ultimately, it all starts with you, the consumer. Have you ever thought about how tea is made? Changing the austere and unappealing new tea leaves into an invigorating and refreshing beverage that we now enjoy and love is no easy task; it is a complicated journey with different stages and procedures. Here, we will venture into a mind-boggling quest to dissect the complex tea courses, discover different groups, investigate the ways leaves are treated, and identify the factors that influence the signature color and taste.
Tea, like some types of food, is categorized as black, green, white, and oolong.
Ways into the mystery of tea are opened by looking into the types of tea before actual tea making is discussed. One of the most popular varieties is black tea, for example. Green, oolong, and white are also widely recognized types. This group includes the tea leaf "Camellia sinensis," but they are separated by different methods of processing, which affect the tea's organoleptic properties and its possible health benefits.
What is the dark tea processing process as a whole?
In the first place, the newly culled tea leaves are wilted, which permits them to lose moisture and become more malleable. Then, the leaves go through rolling or smashing, which separates the cell walls and starts oxidation. During the oxidation cycle, catalysts in the leaves cooperate with oxygen, making the leaves turn a rich, dim earthy tone and fostering the trademark powerful kind of dark tea. At last, the oxidized leaves are warmed to stop the oxidation cycle and then arranged, evaluated, and bundled to be purchased.
How is tea produced?
Unlike dark tea, green tea leaves are subject to a correspondingly lesser breakdown reaction; this helps them to preserve the healthy shade of green and the vivid, pea-like flavor. As an overview of green tea’s information, we will discuss the special methods employed to process it. Once the leaves of tea are culled, they start to wilt and are thereafter warmed up through steaming or heating up in a frying pan or pan. By centering the heating system and defrosting the agents that catalyze oxidation, the juvenile leaves get the green color. The leaves are covered, molded into ones, and dried for viability and packaging.
To begin with, what does the process of making oolong tea involve?
Oolong tea is a semi-oxidized one, which is halfway between green and dark tea in terms of treatment, coloring, and flavoring features. To learn how oolong tea is made, we will go deep into the key processes that make the tea special. Being cut and twisted, the leaves go through becoming bruised or get embraced into the oxidation process. Contrary to another extreme, green tea this time, the oxidation is stopped mid-way, thus creating a slightly oxidized dry leaf.
How is white tea made?
White tea is one of the most fragile and negligibly handled tea assortments. To comprehend how white tea is made, we should take a gander at the exceptional collection and handling techniques utilized. White tea is produced using the most youthful, most delicate buds and leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, which are cautiously hand-culled in late winter. The buds and leaves are then air-dried in a concealed climate, going through negligible handling and oxidation. This delicate methodology safeguards the fragile flavors and smells of the tea, bringing about a pale, unobtrusively sweet, and reviving blend.
The Significance of Tea Handling
Understanding how tea is made fulfills our interest as well as the significance of appropriate handling in deciding the last flavor, fragrance, and nature of the tea. Each move toward the handling
venture, from wilting and moving to oxidation and drying, assumes a vital part in molding the extraordinary qualities of the tea assortment.
Features Touching Tea Flavor and Quality
Developing Circumstances: The environment, soil, and elevation at which the tea plants are developed can fundamentally affect the substance organization and kind of the leaves.
Gathering Procedures: The timing and strategy for collecting the tea leaves can influence their newness, delicacy, and by and large quality.
Handling Hardware: The kind of gear utilized for rolling, oxidation, and drying can impact the consistency and proficiency of the handling steps.
Mixing and Evaluating: Numerous tea assortments are mixed from various groups or reviewed given leaf size and quality, further upgrading their flavor profile.
Instructions to Make Tea at Home
Now that we comprehend how tea is made on a business scale, we should investigate how to make tea at home for a brilliant and invigorating drink.
Begin with top-notch tea leaves. Pick new, great tea leaves from trustworthy sources to guarantee the best flavor and fragrance.
Measure Tea Leaves Precisely: Utilize the suggested measure of tea leaves for the ideal strength and flavor. For the most part, 1 teaspoon of free-leaf tea per 6–8 ounces (180-240 ml) of water is a decent beginning stage.
Steep for the Suitable Time: Every tea assortment has an ideal soaking time to remove the ideal flavors and fragrances without turning out to be harsh or astringent. Follow the suggested soaking times on the tea bundling or consult a tea guide.
Utilize Great Tea Products: Put resources into top-notch tea products, like tea kettles, injectors, and cups, to upgrade the tea-drinking experience and value the full flavor and smell of the tea.
Instructions to Utilize Tea
Cooking and Baking: Integrate tea leaves or agitated tea into recipes for added flavor and fragrance. Tea can be used in marinades, sauces, prepared products, and even frozen yogurt or sorbet.
Tea mixed drinks and fake tails: a trial with tea-injected mixed drinks and fake tails for an extraordinary and reviving turn on exemplary beverages.
Tea-Imbued Sweets: Upgrade the kind of pastries by utilizing tea-implanted milk, cream, or different fixings in recipes for custards, panna cotta, or mousses.
Tea-Based Drinks: Investigate the universe of tea-based refreshments, like air pocket tea, Thai chilled tea, or match lattes, for an invigorating and delightful wind on customary tea.
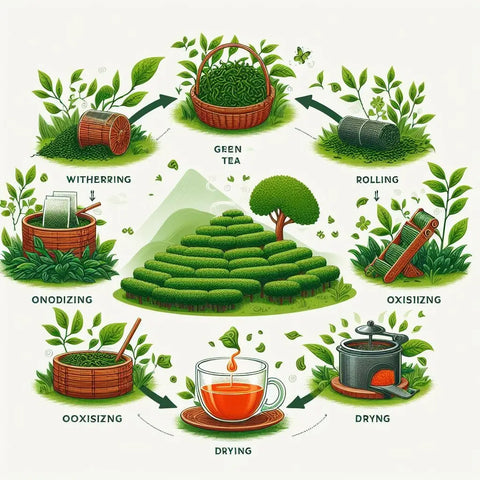

Final Words
Understanding how tea is made is an excursion that reveals the intricacy and masterfulness behind this cherished refreshment. From the culling of new tea passes on to the complex handling strategies, each step assumes a pivotal role in fostering the unmistakable flavors, fragrances, and qualities of the different tea assortments.
FAQs
Might I at any point add milk or sugar to a wide range of teas?
Sometimes milk and sugar are usually added to dark tea; it's by and large not suggested for green, white, or fragile oolong teas. The expansion of milk or sugar can overwhelm the unobtrusive varieties of these teas. Nonetheless, go ahead and examine and track down your inclination.
Is it better to utilize free-leaf tea or tea sacks?
Numerous tea specialists favor free-leaf tea since it is considered superior to the soaking system and frequently brings about a more tasty and fragrant cup. Notwithstanding, tea packs can be a helpful choice for individuals who lean toward a faster and more clear blending technique.





Leave a comment